Difan Zou
DLM-Scope: Mechanistic Interpretability of Diffusion Language Models via Sparse Autoencoders
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have become a standard tool for mechanistic interpretability in autoregressive large language models (LLMs), enabling researchers to extract sparse, human-interpretable features and intervene on model behavior. Recently, as diffusion language models (DLMs) have become an increasingly promising alternative to the autoregressive LLMs, it is essential to develop tailored mechanistic interpretability tools for this emerging class of models. In this work, we present DLM-Scope, the first SAE-based interpretability framework for DLMs, and demonstrate that trained Top-K SAEs can faithfully extract interpretable features. Notably, we find that inserting SAEs affects DLMs differently than autoregressive LLMs: while SAE insertion in LLMs typically incurs a loss penalty, in DLMs it can reduce cross-entropy loss when applied to early layers, a phenomenon absent or markedly weaker in LLMs. Additionally, SAE features in DLMs enable more effective diffusion-time interventions, often outperforming LLM steering. Moreover, we pioneer certain new SAE-based research directions for DLMs: we show that SAEs can provide useful signals for DLM decoding order; and the SAE features are stable during the post-training phase of DLMs. Our work establishes a foundation for mechanistic interpretability in DLMs and shows a great potential of applying SAEs to DLM-related tasks and algorithms.
ProFlow: Zero-Shot Physics-Consistent Sampling via Proximal Flow Guidance
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Inferring physical fields from sparse observations while strictly satisfying partial differential equations (PDEs) is a fundamental challenge in computational physics. Recently, deep generative models offer powerful data-driven priors for such inverse problems, yet existing methods struggle to enforce hard physical constraints without costly retraining or disrupting the learned generative prior. Consequently, there is a critical need for a sampling mechanism that can reconcile strict physical consistency and observational fidelity with the statistical structure of the pre-trained prior. To this end, we present ProFlow, a proximal guidance framework for zero-shot physics-consistent sampling, defined as inferring solutions from sparse observations using a fixed generative prior without task-specific retraining. The algorithm employs a rigorous two-step scheme that alternates between: (\romannumeral1) a terminal optimization step, which projects the flow prediction onto the intersection of the physically and observationally consistent sets via proximal minimization; and (\romannumeral2) an interpolation step, which maps the refined state back to the generative trajectory to maintain consistency with the learned flow probability path. This procedure admits a Bayesian interpretation as a sequence of local maximum a posteriori (MAP) updates. Comprehensive benchmarks on Poisson, Helmholtz, Darcy, and viscous Burgers' equations demonstrate that ProFlow achieves superior physical and observational consistency, as well as more accurate distributional statistics, compared to state-of-the-art diffusion- and flow-based baselines.
Learning Diffusion Policy from Primitive Skills for Robot Manipulation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Diffusion policies (DP) have recently shown great promise for generating actions in robotic manipulation. However, existing approaches often rely on global instructions to produce short-term control signals, which can result in misalignment in action generation. We conjecture that the primitive skills, referred to as fine-grained, short-horizon manipulations, such as ``move up'' and ``open the gripper'', provide a more intuitive and effective interface for robot learning. To bridge this gap, we propose SDP, a skill-conditioned DP that integrates interpretable skill learning with conditional action planning. SDP abstracts eight reusable primitive skills across tasks and employs a vision-language model to extract discrete representations from visual observations and language instructions. Based on them, a lightweight router network is designed to assign a desired primitive skill for each state, which helps construct a single-skill policy to generate skill-aligned actions. By decomposing complex tasks into a sequence of primitive skills and selecting a single-skill policy, SDP ensures skill-consistent behavior across diverse tasks. Extensive experiments on two challenging simulation benchmarks and real-world robot deployments demonstrate that SDP consistently outperforms SOTA methods, providing a new paradigm for skill-based robot learning with diffusion policies.
Differentiable Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The design of effective reward functions presents a central and often arduous challenge in reinforcement learning (RL), particularly when developing autonomous agents for complex reasoning tasks. While automated reward optimization approaches exist, they typically rely on derivative-free evolutionary heuristics that treat the reward function as a black box, failing to capture the causal relationship between reward structure and task performance. To bridge this gap, we propose Differentiable Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning (DERL), a bilevel framework that enables the autonomous discovery of optimal reward signals. In DERL, a Meta-Optimizer evolves a reward function (i.e., Meta-Reward) by composing structured atomic primitives, guiding the training of an inner-loop policy. Crucially, unlike previous evolution, DERL is differentiable in its metaoptimization: it treats the inner-loop validation performance as a signal to update the Meta-Optimizer via reinforcement learning. This allows DERL to approximate the "meta-gradient" of task success, progressively learning to generate denser and more actionable feedback. We validate DERL across three distinct domains: robotic agent (ALFWorld), scientific simulation (ScienceWorld), and mathematical reasoning (GSM8k, MATH). Experimental results show that DERL achieves state-of-the-art performance on ALFWorld and ScienceWorld, significantly outperforming methods relying on heuristic rewards, especially in out-of-distribution scenarios. Analysis of the evolutionary trajectory demonstrates that DERL successfully captures the intrinsic structure of tasks, enabling selfimproving agent alignment without human intervention.
Towards Theoretical Understanding of Transformer Test-Time Computing: Investigation on In-Context Linear Regression
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Using more test-time computation during language model inference, such as generating more intermediate thoughts or sampling multiple candidate answers, has proven effective in significantly improving model performance. This paper takes an initial step toward bridging the gap between practical language model inference and theoretical transformer analysis by incorporating randomness and sampling. We focus on in-context linear regression with continuous/binary coefficients, where our framework simulates language model decoding through noise injection and binary coefficient sampling. Through this framework, we provide detailed analyses of widely adopted inference techniques. Supported by empirical results, our theoretical framework and analysis demonstrate the potential for offering new insights into understanding inference behaviors in real-world language models.
Self-Contradiction as Self-Improvement: Mitigating the Generation-Understanding Gap in MLLMs
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Despite efforts to unify multimodal generation and understanding tasks in a single model, we show these MLLMs exhibit self-contradiction where generation produces images deemed misaligned with input prompts based on the model's own understanding. We define a Nonunified score that quantifies such self-contradiction. Our empirical results reveal that the self-contradiction mainly arises from weak generation that fails to align with prompts, rather than misunderstanding. This capability asymmetry indicates the potential of leveraging self-contradiction for self-improvement, where the stronger model understanding guides the weaker generation to mitigate the generation-understanding gap. Applying standard post-training methods (e.g., SFT, DPO) with such internal supervision successfully improves both generation and unification. We discover a co-improvement effect on both generation and understanding when only fine-tuning the generation branch, a phenomenon known in pre-training but underexplored in post-training. Our analysis shows improvements stem from better detection of false positives that are previously incorrectly identified as prompt-aligned. Theoretically, we show the aligned training dynamics between generation and understanding allow reduced prompt-misaligned generations to also improve mismatch detection in the understanding branch. Additionally, the framework reveals a potential risk of co-degradation under poor supervision-an overlooked phenomenon that is empirically validated in our experiments. Notably, we find intrinsic metrics like Nonunified score cannot distinguish co-degradation from co-improvement, which highlights the necessity of data quality check. Finally, we propose a curriculum-based strategy based on our findings that gradually introduces harder samples as the model improves, leading to better unification and improved MLLM generation and understanding.
On the Mechanism of Reasoning Pattern Selection in Reinforcement Learning for Language Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated remarkable success in enhancing model capabilities, including instruction-following, preference learning, and reasoning. Yet despite its empirical successes, the mechanisms by which RL improves reasoning abilities remain poorly understood. We present a systematic study of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), showing that its primary benefit comes from optimizing the selection of existing reasoning patterns. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that RLVR-trained models preferentially adopt high-success-rate reasoning patterns while mostly maintaining stable performance on individual patterns. We further develop theoretical analyses on the convergence and training dynamics of RLVR based on a simplified question-reason-answer model. We study the gradient flow and show that RLVR can indeed find the solution that selects the reason pattern with the highest success rate. Besides, our theoretical results reveal two distinct regimes regarding the convergence of RLVR training: (1) rapid convergence for models with relatively strong initial reasoning capabilities versus (2) slower optimization dynamics for weaker models. Furthermore, we show that the slower optimization for weaker models can be mitigated by applying the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) before RLVR, when using a feasibly high-quality SFT dataset. We validate the theoretical findings through extensive experiments. This work advances our theoretical understanding of RL's role in LLM fine-tuning and offers insights for further enhancing reasoning capabilities.
Model Unlearning via Sparse Autoencoder Subspace Guided Projections
May 30, 2025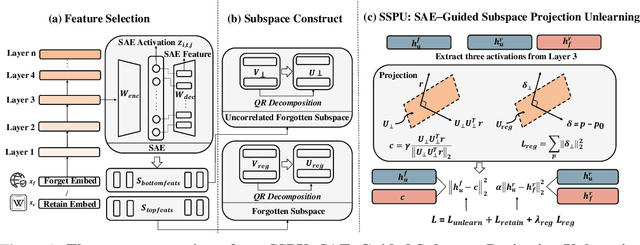
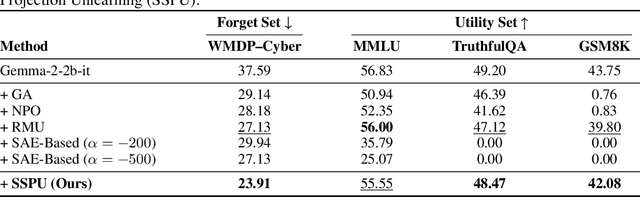
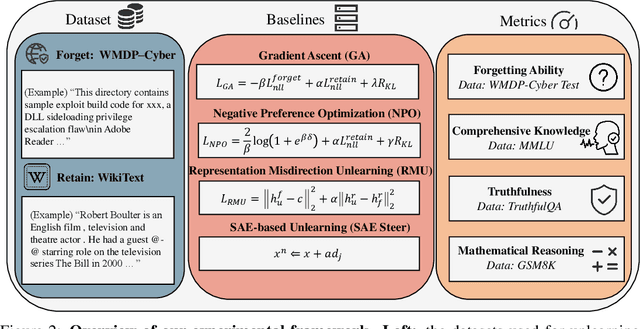
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) store vast amounts of information, making them powerful yet raising privacy and safety concerns when selective knowledge removal is required. Existing unlearning strategies, ranging from gradient-based fine-tuning and model editing to sparse autoencoder (SAE) steering, either lack interpretability or fail to provide a robust defense against adversarial prompts. We propose SAE-Guided Subspace Projection Unlearning (SSPU), a novel framework that leverages SAE features to drive targeted updates in the model's parameter space, enabling precise, interpretable, and robust unlearning. SSPU's three-stage pipeline performs data-driven layer and feature selection, subspace construction via QR decomposition, and constrained optimization that controls activations into an "irrelevant" subspace while preserving retained knowledge. Overall, we use SAE features to construct a subspace that supervises unlearning, refining the loss and adding a regularization term to guide interpretable parameter updates. In experiments on the WMDP-Cyber forget set and three utility benchmarks (MMLU, TruthfulQA, GSM8K), SSPU reduces harmful knowledge accuracy by 3.22% compared to the strongest baseline. It also improves adversarial robustness, lowering malicious accuracy under jailbreak prompts compared to baselines. Our findings expose the limitations of prior unlearning methods and demonstrate how interpretable subspace-guided optimization can achieve robust, controllable model behavior.
Almost Linear Convergence under Minimal Score Assumptions: Quantized Transition Diffusion
May 28, 2025Abstract:Continuous diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable performance in data generation across various domains, yet their efficiency remains constrained by two critical limitations: (1) the local adjacency structure of the forward Markov process, which restricts long-range transitions in the data space, and (2) inherent biases introduced during the simulation of time-inhomogeneous reverse denoising processes. To address these challenges, we propose Quantized Transition Diffusion (QTD), a novel approach that integrates data quantization with discrete diffusion dynamics. Our method first transforms the continuous data distribution $p_*$ into a discrete one $q_*$ via histogram approximation and binary encoding, enabling efficient representation in a structured discrete latent space. We then design a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC) with Hamming distance-based transitions as the forward process, which inherently supports long-range movements in the original data space. For reverse-time sampling, we introduce a \textit{truncated uniformization} technique to simulate the reverse CTMC, which can provably provide unbiased generation from $q_*$ under minimal score assumptions. Through a novel KL dynamic analysis of the reverse CTMC, we prove that QTD can generate samples with $O(d\ln^2(d/\epsilon))$ score evaluations in expectation to approximate the $d$--dimensional target distribution $p_*$ within an $\epsilon$ error tolerance. Our method not only establishes state-of-the-art inference efficiency but also advances the theoretical foundations of diffusion-based generative modeling by unifying discrete and continuous diffusion paradigms.
Physics-Informed Distillation of Diffusion Models for PDE-Constrained Generation
May 28, 2025Abstract:Modeling physical systems in a generative manner offers several advantages, including the ability to handle partial observations, generate diverse solutions, and address both forward and inverse problems. Recently, diffusion models have gained increasing attention in the modeling of physical systems, particularly those governed by partial differential equations (PDEs). However, diffusion models only access noisy data $\boldsymbol{x}_t$ at intermediate steps, making it infeasible to directly enforce constraints on the clean sample $\boldsymbol{x}_0$ at each noisy level. As a workaround, constraints are typically applied to the expectation of clean samples $\mathbb{E}[\boldsymbol{x}_0|\boldsymbol{x}_t]$, which is estimated using the learned score network. However, imposing PDE constraints on the expectation does not strictly represent the one on the true clean data, known as Jensen's Gap. This gap creates a trade-off: enforcing PDE constraints may come at the cost of reduced accuracy in generative modeling. To address this, we propose a simple yet effective post-hoc distillation approach, where PDE constraints are not injected directly into the diffusion process, but instead enforced during a post-hoc distillation stage. We term our method as Physics-Informed Distillation of Diffusion Models (PIDDM). This distillation not only facilitates single-step generation with improved PDE satisfaction, but also support both forward and inverse problem solving and reconstruction from randomly partial observation. Extensive experiments across various PDE benchmarks demonstrate that PIDDM significantly improves PDE satisfaction over several recent and competitive baselines, such as PIDM, DiffusionPDE, and ECI-sampling, with less computation overhead. Our approach can shed light on more efficient and effective strategies for incorporating physical constraints into diffusion models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge